Etcd-Raft Source Code Analysis
Etcd是Go语言实现的基于Raft协议的kv存储,是目前市面上比较成熟的Raft实现。代码层面上,Etcd-Raft模块的封装跟逻辑都是非常优秀的。这里希望学习Etcd 能够更加深入的了解Raft。
Etcd-Raft 模块是一个独立的模块,它按照Raft论文实现了各种协议类型的处理,但对于Entries如何落盘,如何传输等问题都没有涉及。Etcd默认这些逻辑的实现由调Raft模块的调用者来实现。所以,Etcd在Raft模块之上实现了RaftNode,并给出了一个RaftExample。RaftNode封装了一系列的管道跟Etcd-Raft通信,封装了WAL日志管理的接口,快照的接口。RaftExample 又集成了RaftNode模块,Http服务端模块,kvstore模块形成了一个可以对外提供服务的完整实现。RaftExample的结构如下图所示。
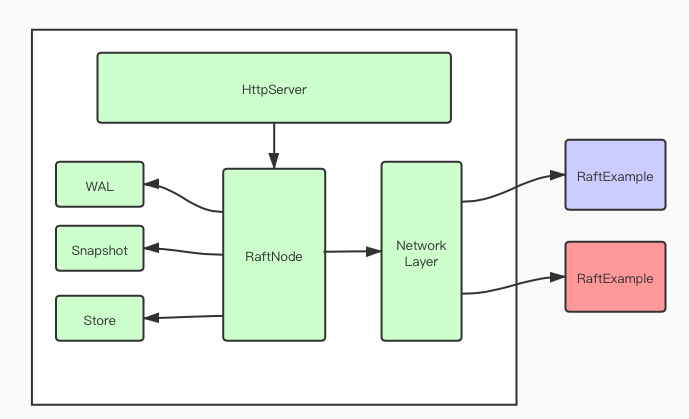
这里会着重于从主要从代码层面来学习Etcd-Raft的实现。关于HttpServer,RaftNode等模块的实现读者可以自己学习一下Etcd的代码,这里不做过多介绍。
0, Etcd-Raft
这里默认读者比较熟悉Raft算法的原理,一些基本的Raft概念可以参考RAFT论文 Leader Election & Log Replication。整个的Etcd-Raft的实现是基本上没有锁的,也就是说只有一个线程在操作这个模块,为了保证效率,Etcd-Raft内部是没有磁盘的操作的,尤其是对于Entry的操作,Etcd-Raft完全是纯内存的操作。下面来看一下Etcd-Raft关于Entry的主要数据结构。
Entry的操作分为两个数据结构,分别是MemoryStorage和Unstable,为了实现Entry的快速访问和修改,Etcd会将没有compact到snapshot的数据保留一份在内存当中,这部分数据分别存在MemstoryStoreage跟unstable中。
MemoryStorage继承于Storage,提供一份可以快速访问的盘上数据的内存拷贝。个人理解应该只是落盘的数据中没有compact到snapshot的entry的内存拷贝,并不是一份完整的库的拷贝。上层模块的逻辑会定时的compact,以至于这个MemoryStorage不会特别大。
需要说明的是这两个数据结构都用到了Term 和Index,对于Term跟Index熟悉Raft的读者肯定不会陌生,这里Etcd-Raft的Term是任期的概念,Index是entries的全局唯一编号,是自增的正整数。下面分别介绍这两个数据结构。
1.1, Storage
Storage 提供了以下接口:
type Storage interface {
// InitialState returns the saved HardState and ConfState information.
InitialState() (pb.HardState, pb.ConfState, error)
// Entries returns a slice of log entries in the range [lo,hi).
// MaxSize limits the total size of the log entries returned, but
// Entries returns at least one entry if any.
Entries(lo, hi, maxSize uint64) ([]pb.Entry, error)
// Term returns the term of entry i, which must be in the range
// [FirstIndex()-1, LastIndex()]. The term of the entry before
// FirstIndex is retained for matching purposes even though the
// rest of that entry may not be available.
Term(i uint64) (uint64, error)
// LastIndex returns the index of the last entry in the log.
LastIndex() (uint64, error)
// FirstIndex returns the index of the first log entry that is
// possibly available via Entries (older entries have been incorporated
// into the latest Snapshot; if storage only contains the dummy entry the
// first log entry is not available).
FirstIndex() (uint64, error)
// Snapshot returns the most recent snapshot.
// If snapshot is temporarily unavailable, it should return
// ErrSnapshotTemporarilyUnavailable,
// so raft state machine could know that Storage needs some time to prepare
// snapshot and call Snapshot later.
Snapshot() (pb.Snapshot, error)
}
具体关注Append方法:
// Append the new entries to storage.
// TODO (xiangli): ensure the entries are continuous and
// entries[0].Index > ms.entries[0].Index
func (ms *MemoryStorage) Append(entries []pb.Entry) error {
if len(entries) == 0 {
return nil
}
ms.Lock()
defer ms.Unlock()
first := ms.firstIndex()
last := entries[0].Index + uint64(len(entries)) - 1
// shortcut if there is no new entry.
if last < first {
return nil
}
// truncate compacted entries
if first > entries[0].Index {
entries = entries[first-entries[0].Index:]
}
offset := entries[0].Index - ms.ents[0].Index
switch {
case uint64(len(ms.ents)) > offset:
ms.ents = append([]pb.Entry{}, ms.ents[:offset]...)
ms.ents = append(ms.ents, entries...)
case uint64(len(ms.ents)) == offset:
ms.ents = append(ms.ents, entries...)
default:
raftLogger.Panicf("missing log entry [last: %d, append at: %d]",
ms.lastIndex(), entries[0].Index)
}
return nil
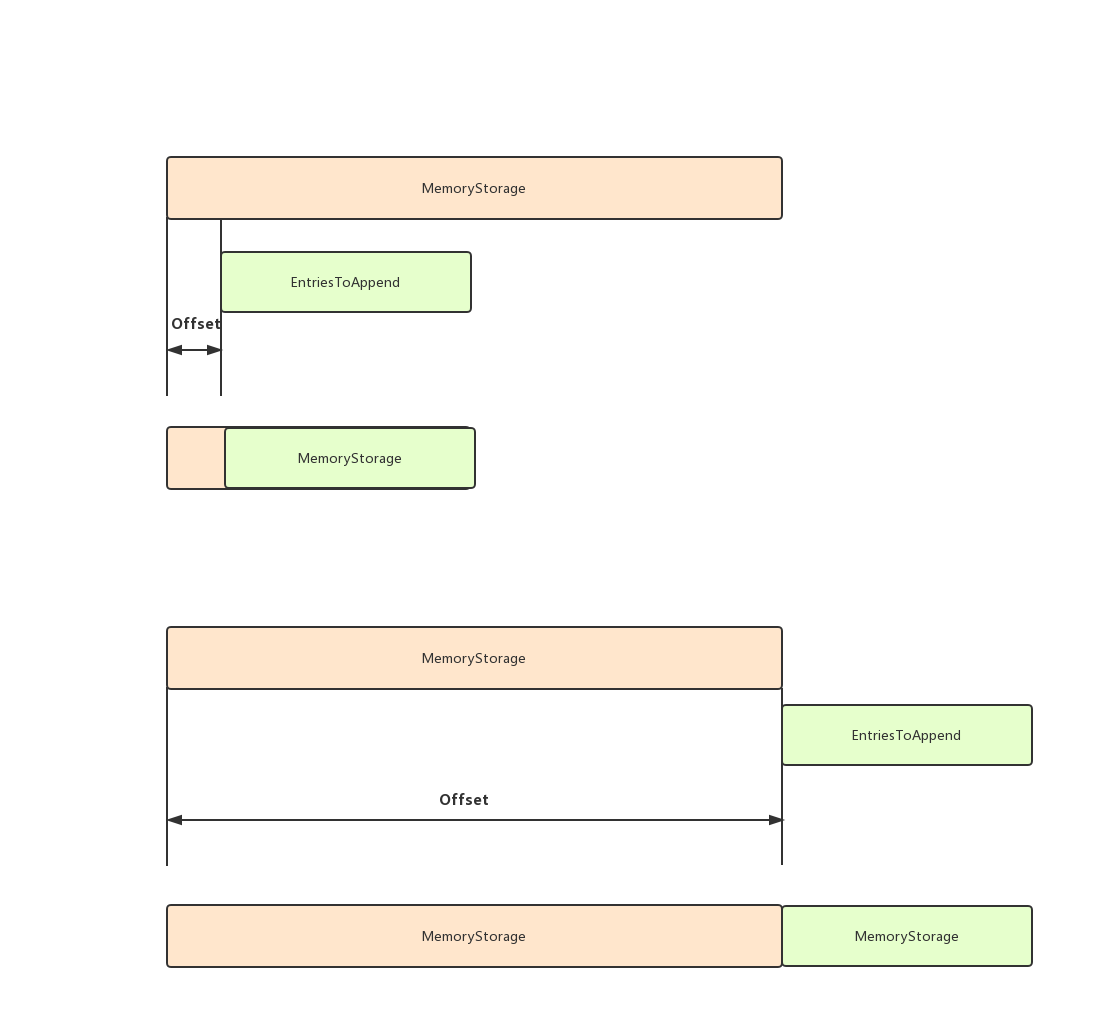
1,如果需要append的entries,有一部分在compact内部,则这部分entries不需要再append
2,计算待append的entries和MemoryStorage的entries的差值,得出offset
3,根据offset进行append
对于Append的两种方式如下图所示:
1.2, Unstable
Unstable 对于主维护了客户端请求对应的Entry记录,对于从来说维护了从主复制来的Entry记录。
// unstable.entries[i] has raft log position i+unstable.offset.
// Note that unstable.offset may be less than the highest log
// position in storage; this means that the next write to storage
// might need to truncate the log before persisting unstable.entries.
type unstable struct {
// the incoming unstable snapshot, if any.
snapshot *pb.Snapshot
// all entries that have not yet been written to storage.
entries []pb.Entry
offset uint64
// record error msg
logger Logger
}
具体关注Append方法:
func (u *unstable) truncateAndAppend(ents []pb.Entry) {
after := ents[0].Index
switch {
case after == u.offset+uint64(len(u.entries)):
// after is the next index in the u.entries
// directly append
u.entries = append(u.entries, ents...)
case after <= u.offset:
u.logger.Infof("replace the unstable entries from index %d", after)
// The log is being truncated to before our current offset
// portion, so set the offset and replace the entries
u.offset = after
u.entries = ents
default:
// truncate to after and copy to u.entries
// then append
u.logger.Infof("truncate the unstable entries before index %d", after)
u.entries = append([]pb.Entry{}, u.slice(u.offset, after)...)
u.entries = append(u.entries, ents...)
}
}
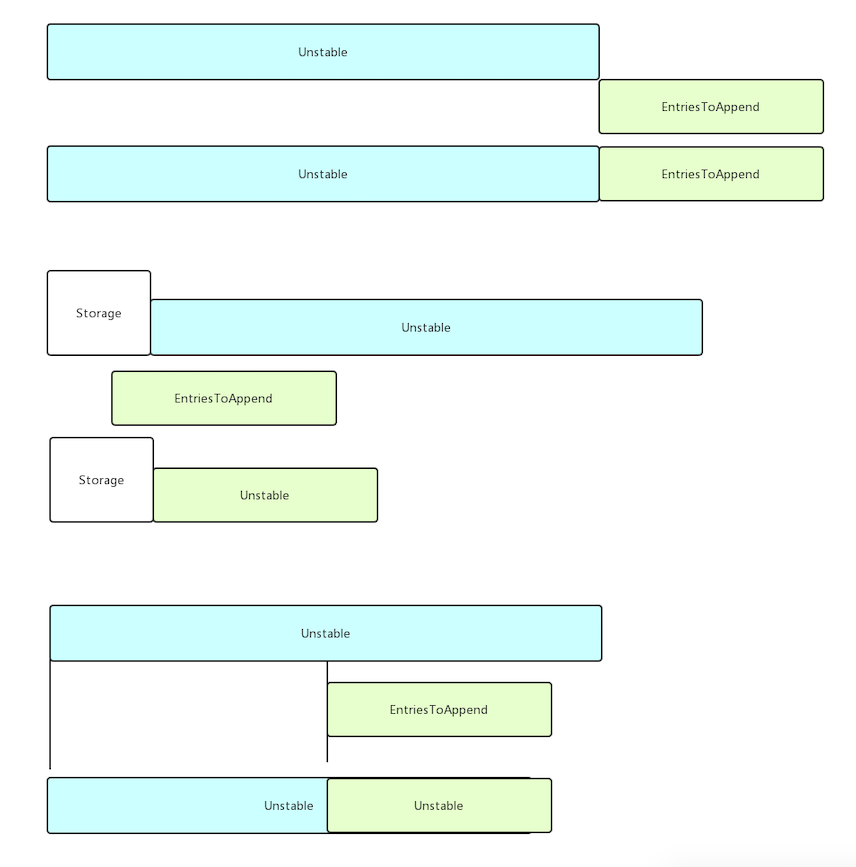
1,获得待添加的entries的起始位置
2,分情况append entries
对于Unstable的Append方式如下图所示:
1.3, RaftLog
RafLogt是SnapShot + MemoryStorage + Unstable的集合,也是真正Raft协议模块调用的模块,他们的组合逻辑如下图所示。

type raftLog struct {
// storage contains all stable entries since the last snapshot.
storage Storage
// unstable contains all unstable entries and snapshot.
// they will be saved into storage.
unstable unstable
// committed is the highest log position that is known to be in
// stable storage on a quorum of nodes.
committed uint64
// applied is the highest log position that the application has
// been instructed to apply to its state machine.
// Invariant: applied <= committed
applied uint64
logger Logger
// maxNextEntsSize is the maximum number aggregate
// byte size of the messages
// returned from calls to nextEnts.
maxNextEntsSize uint64
}
重点关注raftLog的Append操作:
// maybeAppend returns (0, false) if the entries cannot be appended.
// Otherwise, it returns (last index of new entries, true).
func (l *raftLog)
maybeAppend(index, logTerm, committed uint64, ents ...pb.Entry)
(lastnewi uint64, ok bool) {
if l.matchTerm(index, logTerm) {
lastnewi = index + uint64(len(ents))
ci := l.findConflict(ents)
switch {
case ci == 0:
case ci <= l.committed:
l.logger.Panicf("entry %d conflict with committed entry
[committed(%d)]", ci, l.committed)
default:
offset := index + 1
l.append(ents[ci-offset:]...)
}
// AZ: follower behavior
l.commitTo(min(committed, lastnewi))
return lastnewi, true
}
return 0, false
}
func (l *raftLog) append(ents ...pb.Entry) uint64 {
if len(ents) == 0 {
return l.lastIndex()
}
if after := ents[0].Index - 1; after < l.committed {
l.logger.Panicf("after(%d) is out of range [committed(%d)]",
after, l.committed)
}
// AZ: append in unstable only
l.unstable.truncateAndAppend(ents)
return l.lastIndex()
}
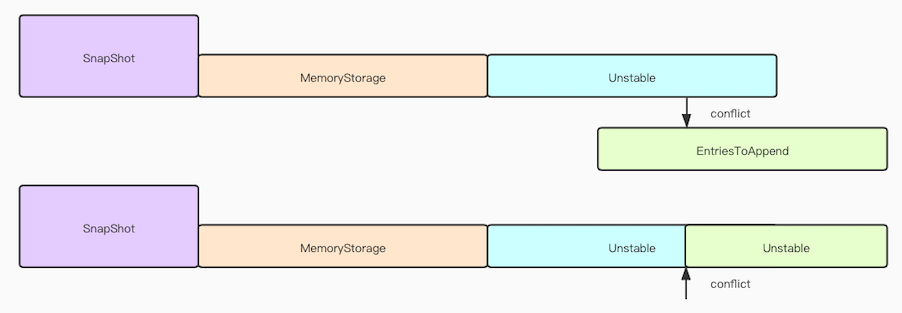
1,查看输入参数index和logTerm跟raftLog下的Entry是否一致
2,找到待添加的entries与raftLog 冲突的位置
3,按照冲突位置进行合并
4,append到unstable当中
Append如下图所示:
// findConflict finds the index of the conflict.
// It returns the first pair of conflicting entries between the existing
// entries and the given entries, if there are any.
// If there is no conflicting entries, and the existing entries contains
// all the given entries, zero will be returned.
// If there is no conflicting entries, but the given entries contains new
// entries, the index of the first new entry will be returned.
// An entry is considered to be conflicting if it has the same index but
// a different term.
// The first entry MUST have an index equal to the argument 'from'.
// The index of the given entries MUST be continuously increasing.
func (l *raftLog) findConflict(ents []pb.Entry) uint64 {
// AZ: check every ents in raftLog, if theie term match
for _, ne := range ents {
if !l.matchTerm(ne.Index, ne.Term) {
if ne.Index <= l.lastIndex() {
l.logger.Infof("found conflict")
}
return ne.Index
}
}
return 0
}
1,遍历待添加的Entry,寻找第一个待添加的Entry 与raftLog 不一致的位置。
以上就是RaftLog Append的实现方法,主要是调用了Unstable的append方法进行追加。介绍完了RaftLog 之后,接下来具体介绍Etcd当中Raft部分的逻辑是如何实现的。
2, Etcd-Raft 算法实现
type raft struct {
id uint64
Term uint64
Vote uint64
prs tracker.ProgressTracker
state StateType
// AZ: step 是一个函数指针,具体的实现由其角色决定
//(stepLeader stepCandidate stepFollower)
step stepFunc
}
对于Raft算法的主要实现是在Raft模块内部实现的。整个Raft模块可以看作是一个消息处理机,处理上层模块的各种消息,包括内部消息和来自follower,leader的外部消息。Etcd-Raft实现的消息类型非常之多,本次就先关注Entries复制相关的消息类型。Raft的消息处理入口函数如下所示。
func (r *raft) Step(m pb.Message) error {
// Handle the message term
// which may result in our stepping down to a follower.
switch {
case m.Term == 0:
// local message
case m.Term > r.Term:
// If a server receives a RequestVote request within the minimum
// election timeout of hearing from a current leader, it does not
// update its term or grant its vote
switch {
// Process Prevote Logic
...
default:
if m.Type == pb.MsgApp || m.Type == pb.MsgHeartbeat
|| m.Type == pb.MsgSnap {
r.becomeFollower(m.Term, m.From)
} else {
r.becomeFollower(m.Term, None)
}
}
case m.Term < r.Term:
if (r.checkQuorum) && (m.Type == pb.MsgHeartbeat ||m.Type == pb.MsgApp) {
r.send(pb.Message{To: m.From, Type: pb.MsgAppResp}) // AZ: with term 0
} else {
// ignore other cases
}
return nil
}
switch m.Type{
// process pb.MsgHup and pb.MsgVote, pb.MsgPreVote
default:
err := r.step(r, m)
if err != nil {
return err
}
}
}
}
Step是Raft模块消息处理的入口参数,根据不同的Message类型进行相应的处理。
1,收到消息Term比当前Term大,则自己变为Follower
2,收到消息Term比当前Term小,则发送MsgAppResp消息
3,通过step挂载的函数(小写的step)对于不同的消息进行下一步的处理
2.1, Leader处理客户端请求
如果节点角色是Leader,step(小写的)挂载stepLeader函数。收到客户端的请求之后,上层模块会封装成MsgProp消息传到step函数当中。处理流程如下:
func stepLeader(r *raft, m pb.Message) error {
switch m.Type {
case pb.MsgProp:
// AZ: check if there is config change pending. If there is one pending,
// drop this proposal.
// AZ: go over m.Entries, to check is there is config change request.
// Merge config changes to be one config change request.
r.appendEntry(m.Entries...)
r.bcastAppend()
}
通过step指针链接到了stepLeader函数内部
1,如果是config change的请求,做特殊处理。
2,调用appendEntry
3,将Entries同步到从
func (r *raft) appendEntry(es ...pb.Entry) (accepted bool) {
li := r.raftLog.lastIndex()
for i := range es {
es[i].Term = r.Term
es[i].Index = li + 1 + uint64(i)
}
// Track the size of this uncommitted proposal.
if !r.increaseUncommittedSize(es) {
// Drop the proposal.
return false
}
// use latest "last" index after truncate/append
li = r.raftLog.append(es...)
r.prs.Progress[r.id].MaybeUpdate(li)
// Regardless of maybeCommit's return, our caller will call bcastAppend.
r.maybeCommit()
return true
}
1,为pb当中的entry添加term 和 index
2,更新uncommitted 数据大小
3,调用raftLog的append
4,调用MaybeUpdate 和maybeCommit更新match index,next index 和 committed index
// bcastAppend sends RPC, with entries to all peers that are not up-to-date
// according to the progress recorded in r.prs.
func (r *raft) bcastAppend() {
r.prs.Visit(func(id uint64, _ *tracker.Progress) {
if id == r.id {
return
}
r.sendAppend(id)
})
}
这里的MsgApp消息等同于Raft论文中的AppendEntriesRPC。
Send MsgApp(Append Entries)
// sendAppend sends an append RPC with new entries (if any) and the
// current commit index to the given peer.
func (r *raft) sendAppend(to uint64) {
term, errt := r.raftLog.term(pr.Next - 1)
ents, erre := r.raftLog.entries(pr.Next, r.maxMsgSize)
// send snapshot if we failed to get term or entries
if errt != nil || erre != nil {
pr.BecomeSnapshot(sindex)
} else {
m.Type = pb.MsgApp
m.Index = pr.Next - 1 // AZ: last_index
m.LogTerm = term // AZ: last_term
m.Entries = ents
m.Commit = r.raftLog.committed
}
r.send(m)
}
2.2, 处理MsgApp消息:
Recv MsgApp && Send MsgAppResp
func stepFollower(r *raft, m pb.Message) error {
switch m.Type {
...
case pb.MsgProp:
if r.lead == None {
r.logger.Infof("%x no leader at term %d; dropping proposal")
return ErrProposalDropped
}
m.To = r.lead
r.send(m)
case pb.MsgApp:
r.electionElapsed = 0
r.lead = m.From
r.handleAppendEntries(m)
...
}
func (r *raft) handleAppendEntries(m pb.Message) {
if m.Index < r.raftLog.committed {
r.send(pb.Message
{To: m.From, Type: pb.MsgAppResp, Index: r.raftLog.committed})
return
}
if mlastIndex, ok := r.raftLog.maybeAppend
(m.Index, m.LogTerm, m.Commit, m.Entries...); ok {
r.send(pb.Message{To: m.From, Type: pb.MsgAppResp, Index: mlastIndex})
} else {
// AZ:maybeAppend failed, last_index last_term not match
r.send(pb.Message
{To: m.From, Type: pb.MsgAppResp, Index: m.Index,
Reject: true, RejectHint: r.raftLog.lastIndex()})
}
}
stepFollower
1,如果是客户端请求,转发到对应的主上。
2,如果是主发来的MsgApp
2.1,如果index 小于 committed 返回 当前的committed index
2.2 调用raftLog maybeAppend
a) 如果成功,返回当前log的last_index
b) 如果失败,发送当前log的last_index
Recv MsgAppRecv
func stepLeader(r *raft, m pb.Message) error {
switch m.Type {
case pb.MsgAppResp:
pr.RecentActive = true
if m.Reject {
if pr.MaybeDecrTo(m.Index, m.RejectHint) {
if pr.State == tracker.StateReplicate {
pr.BecomeProbe()
}
r.sendAppend(m.From)
}
} else {
// AZ: progress update match and next
if pr.MaybeUpdate(m.Index) {
switch {
case pr.State == tracker.StateProbe:
pr.BecomeReplicate()
case pr.State == tracker.StateSnapshot
&& pr.Match >= pr.PendingSnapshot:
// Transition back to replicating state via probing state
// (which takes the snapshot into account). If we didn't
// move to replicating state, that would only happen with
// the next round of appends (but there may not be a next
// round for a while, exposing an inconsistent RaftStatus).
pr.BecomeProbe()
pr.BecomeReplicate()
case pr.State == tracker.StateReplicate:
pr.Inflights.FreeLE(m.Index)
}
// AZ: Update leader committed id
if r.maybeCommit() {
// AZ: if update leader commit success, broadcast to peers
r.bcastAppend()
}
// AZ: send next round of MsgApp
r.maybeSendAppend(m.From, false)
}
}
}
}
func (pr *Progress) MaybeDecrTo(rejected, last uint64) bool {
if pr.State == StateReplicate {
// The rejection must be stale if the progress has matched and "rejected"
// is smaller than "match".
if rejected <= pr.Match {
return false
}
// Directly decrease next to match + 1.
pr.Next = pr.Match + 1
return true
}
return true
}
stepLeader
1,如果Reject,尝试调用MaybeDecrTo回退。MaybeDecrTo(m.Index, m.RejectHint),m.Index 为发送报文的last_index, m.RejectHint 为从的last_index
2,如果接受,更新对应progress中的match 和 next
3,状态转换
4,更新自己的committed id
5,继续发送entries
在Etcd-Raft的Entries复制机制中,提供了StateProbe这样一个状态。对于刚开始日志复制的时候,需要协商主从entries一致的位置,这一状态Etcd-Raft称之为StateProbe。StateProbe阶段,每次MsgApp消息只携带一条entry,直到主从建立了一致的同步点,之后会进入StateReplicate阶段用batch的方式发送Entries。
3, 总结
Etcd-Raft的优化非常之多,本文只是对Etcd-Raft的源码做一个大概的了解。更多的相关逻辑,读者可以自行阅读源码。